Temperature control is a critical part of food safety management for food handlers. Food handlers must always be aware of the temperature at which foods are stored and served, along with the risks posed by fluctuations in temperature.
A breakdown in temperature control can lead to unsafe food handling practices. It may even result in food poisoning or other illnesses.
What Is Temperature Control?
Temperature control for food handlers is the practice of controlling the temperature of food products, so they can be stored and served safely. This can be accomplished by using specialized equipment or developing a system that monitors each product’s temperature.
When temperatures are controlled, food handlers can maintain safe conditions for customers, employees, and themselves. The best way to manage this process is with a temperature-controlled storage unit or freezer cabinet.
These cabinets allow you to regulate temperatures in different areas of the storage unit to ensure that all foods are correctly stored at their ideal temperatures.
Why Is Temperature Control Important?
Temperature control is essential in food handlers because it helps to prevent foodborne illness. Food handlers need to know how to maintain proper temperature control when working with food and ensure that it stays at the desired temperature.
Temperature control is also essential for food handlers because it allows them to monitor the quality of the food they are handling so that they can make sure that it is safe for consumption.
How temperature can affect food safety
Temperature is one of the most critical factors in food safety. It can affect the growth of bacteria, viruses, and parasites that cause foodborne illness.
Foodborne illness is caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites that grow in food if it is not stored at the correct temperature. This can happen if you leave your food out too long or need to refrigerate it properly after cooking it.
The most common bacteria that causes foodborne illness is Listeria monocytogenes, which can be found in raw meat and vegetables. It can also grow in dairy products, such as cheese and milk.
Foodborne illness can be severe, especially for young children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems. Symptoms include vomiting and diarrhea.
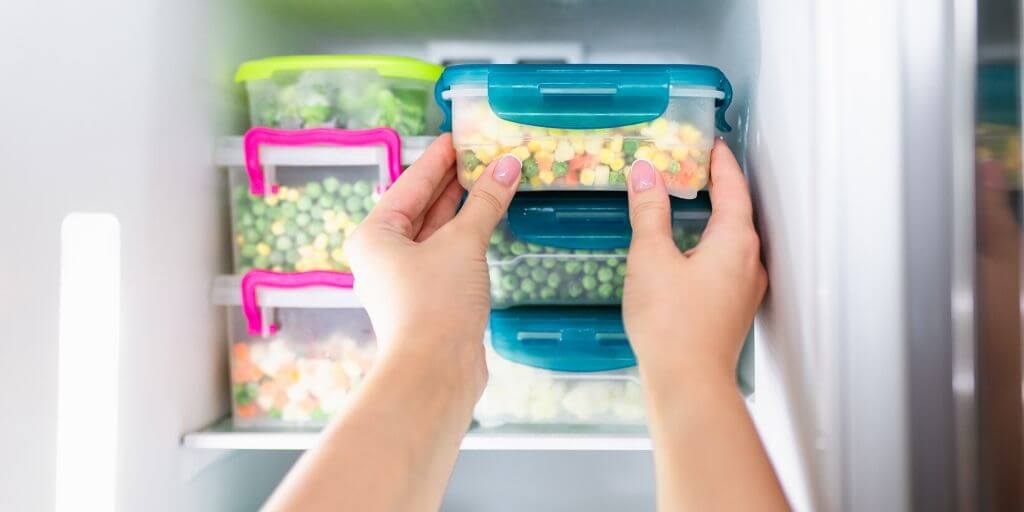
Maintaining proper storage temperatures.
Temperature control is essential for food safety. By maintaining proper storage temperatures, you can ensure that your food doesn’t spoil or become unsafe.
When storing food, it is crucial to maintain proper storage temperatures. The following procedures should be followed when storing food:
- Store the food at the lowest temperature that can be maintained without causing any damage.
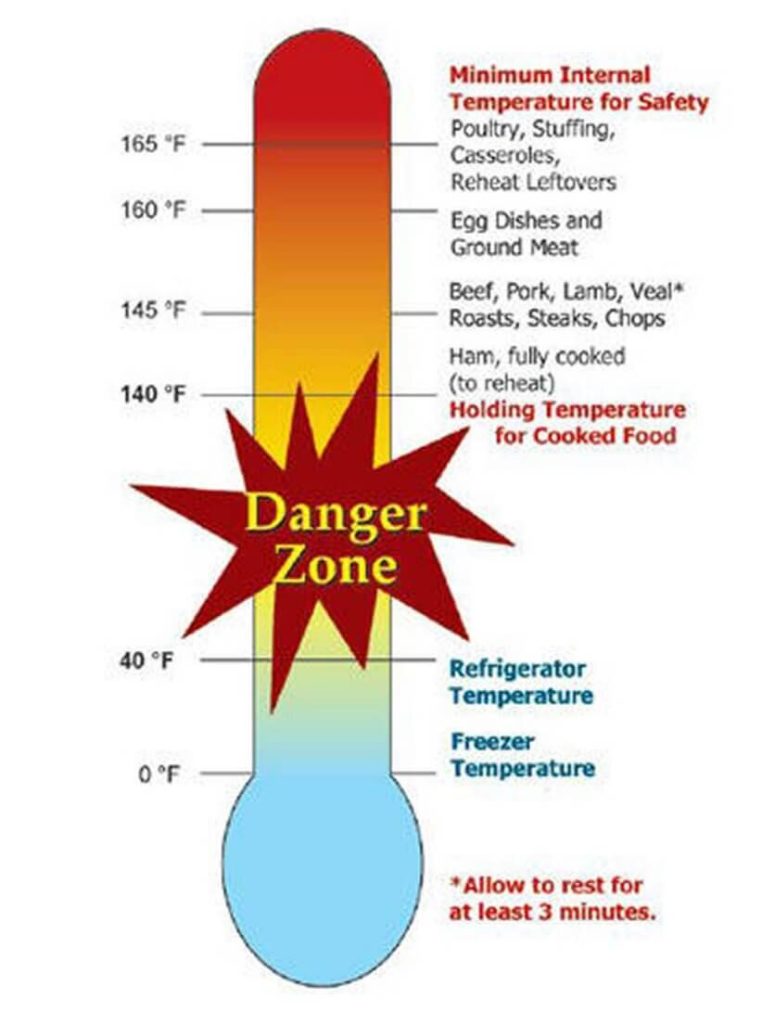
- Ensure that the room temperature is within 4°F to 40°F [2°C to 25°C] of the correct temperature.
- Do not store perishable foods in rooms where they will be exposed to high heat or direct sunlight, as these conditions could cause spoilage or deterioration of the food’s flavor and texture.
- Do not store perishable foods in areas where they may be exposed to high humidity or large amounts of condensation, as these conditions can cause mold and spoilage in food items such as fruits and vegetables, meat products, and fish products.
- Always label perishable foods with their date of purchase, expiry date, storage instructions, and storage conditions so that they are visible and understood by all personnel involved in their handling (e.g., cashiers who handle them at checkout counters).
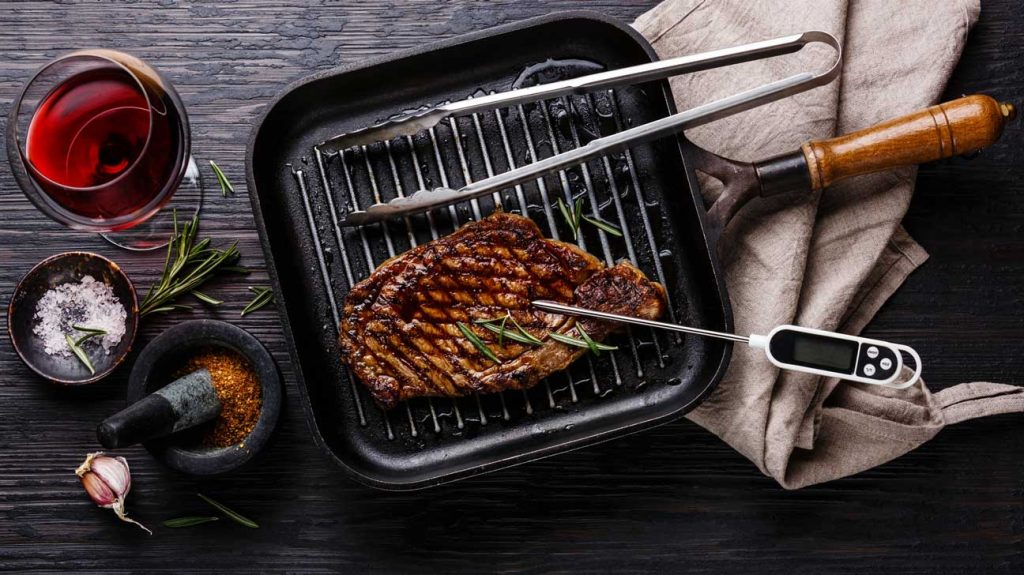
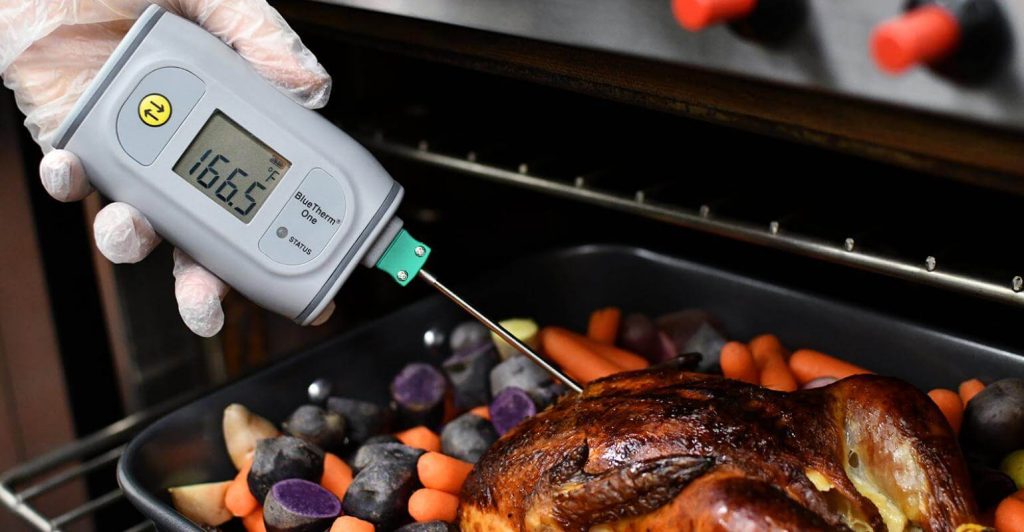
Safe cooking temperatures
If you’re looking to ensure that your food is cooked at the right temperature, these are things you should note:
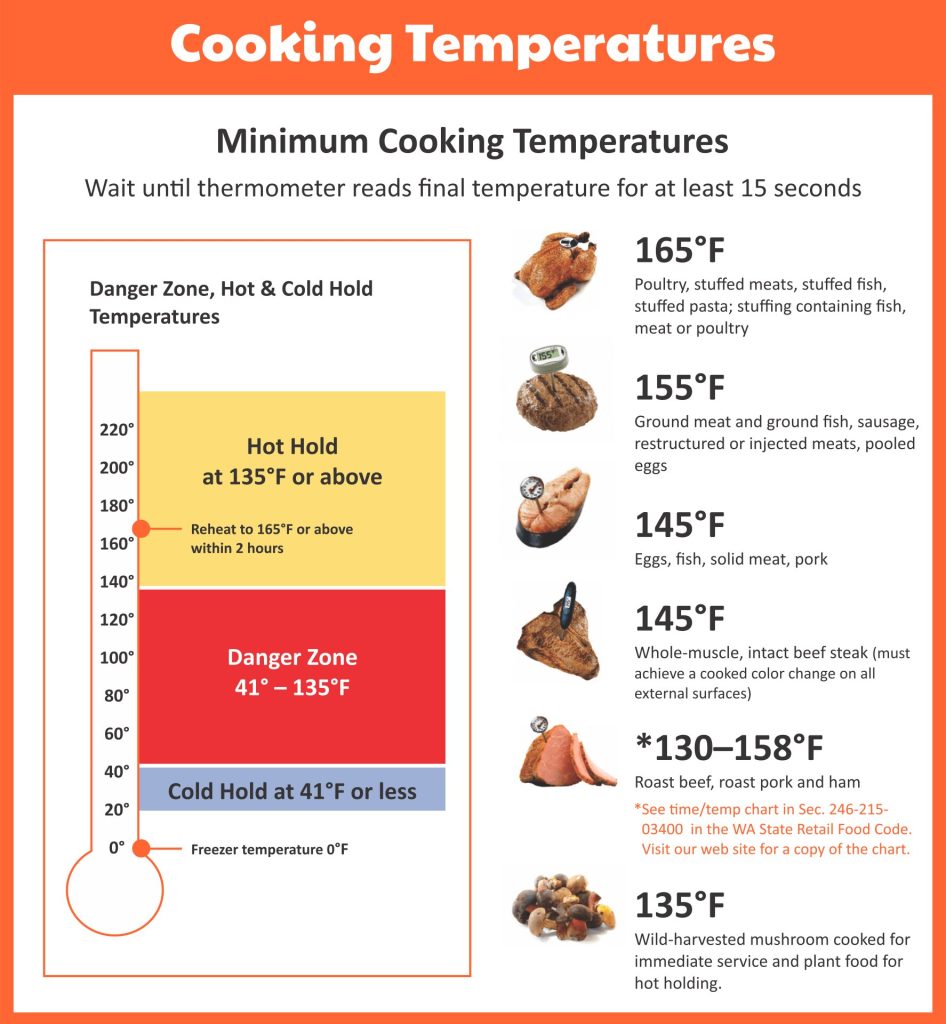
The safe cooking temperature for meat is 165°F.
The safe cooking temperatures for meats should be:
– Steak: 145°F (63°C)
– Pork chops: 145°F (63°C)
– Chicken breasts: 160°F (71°C)
– Ground beef: 160°F (71°C)
The safe cooking temperature for poultry is 165°F.
The safe cooking temperature for fish is 145°F.
High-Risk Food Needing Temperature Control
If you’re working in a restaurant or other food handling facility, some foods are high-risk and require temperature control. High-risk food requiring temperature control includes:
- Meats and poultry
- Fish and shellfish
- Milk and dairy products
- Raw fruits and vegetables
- Eggs
How To Be Mindful Of Temperature Control
- Check the temperature regularly.
- Refrain from relying on memory.
- Please don’t rely on others to do it for you.
- Keep food out of the fridge for a short time, even if it looks okay when checked earlier. The quality may deteriorate over time and cause illness or poisoning.
- Check that temperature first before leaving food in an oven.
Rules And Regulation: Storage, Display, Handling, And Transport Of Temperatures
The food code is a set of rules and regulations that govern the storage, display, handling, and transport of temperatures. It was developed by the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) in 2010 to ensure that all people handling food are trained safely.
The FSMA requires food handlers who work with perishable products such as meat or poultry to wash their hands regularly before each procedure and after touching any surface where bacteria could be present—even if it looks clean!
Because this practice helps prevent cross-contamination across multiple items in your inventory at once (like when you’re making sandwiches), it’s essential for everyone involved in this industry: from farmers growing produce for supermarkets all over town down through retail sales clerks who ship out orders within hours after filling them up at their convenience store locations every day after work hours end…
How To Keep Temperature Records
It is essential to keep track of the temperatures of your food as a food handler so that you can ensure that you are following proper procedures. You should also ensure that all employees have access to a thermometer and a digital or meat thermometer.
If you need access to these tools or are too expensive for your budget, consider using an instant-read food thermometer instead. This type of device is small enough to fit in your pocket and accurate enough for most applications; however, it does require calibration each time it is used (which can take up some time).
Conclusion
Temperature control is a critical part of food safety. Knowing how your product is stored and handled and the temperature required for proper cooking and safe consumption is essential. You can use these tips to become more mindful about keeping records of your food handler procedures so that you can keep track of them at all times.